Customize GraphWin Interactive Interface Example
|
The following example illustates the possibilities to customize the interactive interface of GraphWin. To illustrate the adding
of families of functions to GraphWin we use the functions for
computing components
of graphs. These functions all
have the same interface. They take a graph and compute node
arrays of void call_comp(GraphWin& gw, int (*comp)
(const graph& G, node_array<int>& compnum));
|
|
To illustrate adding simple
functions to GraphWin we use DFS
and spanning trees
with the following simple functions.
void dfs_num(GraphWin& gw);
void span_tree(GraphWin& gw);
In the main() function we define a GraphWin gw,
add our simple calls, add a reset button as an example of adding
a member function call, and finally create a sub-menu for the
components functions. We also delete some of the standard menus to
illustrate changing the GraphWin
standard menu.
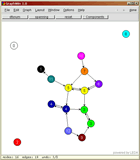
On the right there is a screenshot of the program. Clicking on the picture shows the window in original size. |
 |
Here is the complete program:
#include <LEDA/graphics/graphwin.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/graph.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/basic_graph_alg.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/node_array.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/graph_alg.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/graph_misc.h>
using namespace leda;
void call_comp(GraphWin& gw, int (*comp)(const graph& G,
node_array<int>& compnum))
{
graph& G=gw.get_graph();
node_array<int> compnum(G);
comp(G,compnum);
node v;forall_nodes(v,G) {
int i=compnum[v];
gw.set_label(v,string("%d",i));
gw.set_color(v,(color)(i%16));
}
if (gw.get_flush()==false) gw.redraw();
}
void dfs_num(GraphWin& gw)
{
graph& G=gw.get_graph();
node_array<int> dfsnum(G);
node_array<int> compnum(G);
DFS_NUM(G,dfsnum,compnum);
node v;forall_nodes(v,G)
gw.set_label(v,string("%d|%d",dfsnum[v],compnum[v]));
if (gw.get_flush()==false) gw.redraw();
}
void span_tree(GraphWin& gw)
{
graph& G=gw.get_graph();
list<edge> L=SPANNING_TREE(G);
gw.set_color(L,red); gw.set_width(L,2);
if (gw.get_flush()==false) gw.redraw();
}
int main()
{
GraphWin gw;
//add two simple function calls,
gw.add_simple_call(dfs_num, "dfsnum");
gw.add_simple_call(span_tree, "spanning");
//a member function call, and a
gw.add_member_call(&GraphWin::reset,"reset");
//menu with three non-simple functions using
//a common call function
int menu1=gw.add_menu("Components");
gw_add_call(gw,COMPONENTS,call_comp,
"simply connected", menu1);
gw_add_call(gw,COMPONENTS1,call_comp,
"simply connected1", menu1);
gw_add_call(gw,STRONG_COMPONENTS,call_comp,
"strongly connected", menu1);
//we delete some of the standard menus,
gw.set_default_menu(M_COMPLETE & ~M_HELP);
gw.display(); gw.edit();
gw.get_window().screenshot("customize_ii");
return 0;
}
|
|
See also:
Customizing the Interactive Interface
Adding GraphWin Member Functions
Changing the GraphWin standard menu
Depth First Search and Breadth First Search