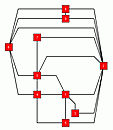
Example ORTHO_EMBEDDING()
|
Let |
|
|
We first generate a random planar graph Then we define Using these parameters we call |
|
#include <LEDA/graph/graph.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/graph_draw.h>
#include <LEDA/graphics/graphwin.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/node_array.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/edge_array.h>
#include <LEDA/core/list.h>
using namespace leda;
int main()
{
graph G;
random_planar_graph(G,10,20);
Make_Connected(G);
list<edge> dummy_edges;
Make_Bidirected(G,dummy_edges);
G.make_planar_map();
node_array<double> xpos(G), ypos(G);
edge_array<list<double> > xbends(G), ybends(G);
ORTHO_EMBEDDING(G,xpos,ypos,xbends,ybends);
edge e; forall(e,dummy_edges) G.del_edge(e);
GraphWin gw(G);
gw.set_node_shape(rectangle_node);
gw.set_node_color(red);
double dx, dy, f;
gw.fill_win_params(xpos,ypos,xbends,ybends,dx,dy,f,f);
gw.transform_layout(xpos,ypos,xbends,ybends,dx,dy,f,f);
gw.set_layout(xpos,ypos,xbends,ybends);
gw.open(); gw.display();
return 0;
}
See also:
Manual Entries:
Manual Page Graph Drawing Algorithms