Edit and Run: A Simple Recipe for Interactive Demos with GraphWin
The Edit-and-Run ParadigmThe edit-and-run paradigm for interactive demos of graph
algorithms looks as follows. We define a If you want to show the result of a graph algorithm while you are editing the graph (without clicking the done-button), have a look at A Recipe for Online Demos of Graph Algorithms. If your graph has edge capacities or costs have a look at A Recipe for Online Demos of Network Algorithms. #include <LEDA/graphics/graphwin.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/graph_alg.h>
using namespace leda;
int main()
{
GraphWin gw("Edit-and-Run Paradigm");
gw.display(window::center,window::center);
while (gw.edit()) {
graph& G=gw.get_graph();
//run graph algorithm on G and display result
}
return 0;
}
|
|
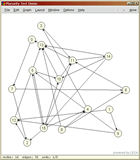
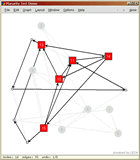
Planarity Testing with Edit-and-RunWe use the edit-and-run paradigm to test the On the right you see screenshots of the program for a non-planar
graph. The first picture shoows the original graph and the second
picture the result of the #include <LEDA/graphwin.h> #include <LEDA/graph_alg.h> using namespace leda; //run graph algorithm and display result void run_and_display(GraphWin& gw); |
|
int main()
{
GraphWin gw("Planarity Test Demo");
gw.display(window::center,window::center);
while (gw.edit()) {
gw.get_window().screenshot("gw_planarity_original");
run_and_display(gw);
}
return 0;
}
//plandemo highlight
void highlight(GraphWin& gw, const list<node>& V,
const list<edge>& E,node_array<int>& kind);
void run_and_display(GraphWin& gw)
{
graph& G=gw.get_graph();
if (PLANAR(G)) {
if (G.number_of_nodes()<3) return;
node_array<double> xcoord(G);
node_array<double> ycoord(G);
STRAIGHT_LINE_EMBEDDING(G,xcoord,ycoord);
gw.adjust_coords_to_win(xcoord,ycoord);
gw.set_layout(xcoord,ycoord);
}
else {
list<node> V_k;list<edge> E_k;
node_array<int> kind(G);
KURATOWSKI(G,V_k,E_k,kind);
gw.save_all_attributes();
highlight(gw,V_k,E_k,kind);
gw.wait("This graph is not planar. I show you a \
Kuratowski subdivision (click done).");
gw.restore_all_attributes();
}
}
void highlight(GraphWin& gw, const list<node>& V,
const list<edge>& E,node_array<int>& kind)
{
const graph& G=gw.get_graph();
bool flush0=gw.set_flush(false);
node v;forall_nodes(v,G) {
switch (kind[v]) {
case 0: gw.set_color(v,grey1);
gw.set_border_color(v,grey1);
gw.set_label_color(v,grey2);
break;
case 2: gw.set_color(v,grey1);
gw.set_label_type(v,no_label);
gw.set_width(v,8);
gw.set_height(v,8);
break;
case 3:
case 4: gw.set_shape(v,rectangle_node);
gw.set_color(v,red);
break;
case -3: gw.set_shape(v,rectangle_node);
gw.set_color(v,blue2);
break;
}
}
edge e;
forall_edges(e,G) gw.set_color(e,grey1);
forall(e,E) {
gw.set_color(e,black);
gw.set_width(e,2);
}
gw.redraw();
gw.set_flush(flush0);
gw.get_window().screenshot("gw_planarity_highlight");
}
|
|
See also:
A Recipe for Online Demos of Graph Algorithms
A Recipe for Online Demos of Network Algorithms