Example Triangulation
|
The following program generates a On the right there is a screenshot of the program. Clicking on
the picture shows the |
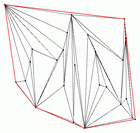 |
#include <LEDA/core/list.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/rat_point.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/random_rat_point.h>
#include <LEDA/graphics/window.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/geo_alg.h>
using namespace leda;
int main()
{
list<rat_point> L;
random_points_in_square(25,100,L);
GRAPH<rat_point,int> G;
edge edgeOnConvexHull=TRIANGULATE_POINTS(L,G);
if (Is_Triangulation(G)) std::cout << "G is a Triangulation\n";
else std::cout << "WARNING: G is no Triangulation!\n";
window W;
W.init(-110,110,-110);
W.open(); W.display();
W.set_node_width(2);
rat_point p; //draw points in L
forall(p,L) {W.draw_filled_node(p.to_point(),black);}
W.read_mouse();
edge e;
forall_edges(e,G) {
point p=G[G.source(e)].to_point();
point q=G[G.target(e)].to_point();
W.draw_edge(p,q);
}
W.read_mouse();
W.set_line_width(2);
e=edgeOnConvexHull;
do {
point p=G[G.source(e)].to_point();
point q=G[G.target(e)].to_point();
W.draw_filled_node(p.to_point(),red);
W.draw_edge(p,q,red);
e=G.face_cycle_succ(e);
} while (e!=edgeOnConvexHull);
W.read_mouse();
W.screenshot("triangulation");
return 0;
}
See also:
Verification of Geometric Structures