Example Delaunay Triangulation
The following program generates alist
L of 25 rat_points in the square (-100,-100,100,100)
and computes a (furthest site) Delaunay triangulation of L
represented by the parametrized graph
G. It also calls Is_Delaunay_Triangulation() to
verify the result. Then it draws the points of L and edges
of the triangulation in black. Finally it shows the convex
hull by drawing the points and edges on the convex hull in red.
|
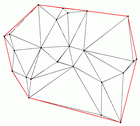
On the right you see a screenshot of the program showing a Delaunay
triangulation of a set of points in the plane, the points and
edges on the convex hull are drawn in red. Clicking on the picture
shows the |
 |
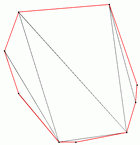
On the right you see a screenshot of the program showing a furthest
site Delaunay triangulation of a set of points in the plane, the
points and edges on the convex hull are drawn in red. For the furthest
site Delaunay diagram all points need to lie on the convex hull. Clicking
on the picture shows the window
in original size. |
 |
#include <LEDA/core/list.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/rat_point.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/random_rat_point.h>
#include <LEDA/graphics/window.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/geo_alg.h>
using namespace leda;
int main()
{
list<rat_point> L;
random_points_in_square(25,100,L);
GRAPH<rat_point,int> G;
delaunay_voronoi_kind kind;
DELAUNAY_TRIANG(L,G);
kind=NEAREST;
//L=CONVEX_HULL(L);
//F_DELAUNAY_TRIANG(L,G); //Furthest Point Delaunay Triangulation
//kind=FURTHEST;
if (Is_Delaunay_Triangulation(G,kind))
std::cout << "G is a Delaunay Triangulation" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "WARNING: G is no Delaunay Triangulation!" << std::endl;
window W;
W.init(-110,110,-110);
W.open(); W.display();
W.set_node_width(2);
rat_point p; //draw points in L
forall(p,L) {W.draw_filled_node(p.to_point(),black);}
W.read_mouse();
edge e;
forall_edges(e,G) { //Delaunay Triangulation
point p=G[G.source(e)].to_point();
point q=G[G.target(e)].to_point();
W.draw_edge(p,q);
}
W.set_line_width(2);
forall_edges(e,G) { //convex hull
point p=G[G.source(e)].to_point();
point q=G[G.target(e)].to_point();
if (G[e]==2) W.draw_edge(p,q,red);
}
W.read_mouse();
W.screenshot("delaunay_triangulation");
return 0;
}
See also:
Verification of Geometric Structures